Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (Šeimyniškių g. 19C)
Šeimyniškių g. 19C, Vilnius
Hila
V. Grybo g. 32A, Vilnius, Lithuania
7:00 - 20:00
MRT examinations performed until 21.00
8:00 - 15:00
MRI examination schedule - 7.00-19.00
9:00 - 15:00
Only MRI examinations!
The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free parking to the right of the building. Drive up to the barrier, wait for the guard to lift it, and enter the site.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Family Medicine
Estų g. 1, Vilnius
8.00–20.00 val.
The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free car parking is available in the shopping center's lot.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Family Medicine
Laisvės pr. 10A, Vilnius, Lithunia (B building)
8.00 - 20.00

The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free parking - in reserved places in front of the entrance to the center.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Šeimos medicinos centras (Bičiulių g.36)
Bičiulių g. 36, Vilniaus r. sav.
07.00 – 20.00 val.
nedirbame
Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (V. Grybo g. 32A)
V. Grybo g. 32A, Vilnius
7.00–20.00 val.
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Free car parking is available on the right side of the building.
Drive up to the barrier, wait for security to lift it, and enter the parking lot.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine
Lvivo g. 101, Vilnius, Lithuania
8.00 - 20.00
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Paid parking - UNIPARK and ParkTown. Read instructions

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine
Estų g. 1, Vilnius
7.00-20.00 val.
9.00-15.00 val.
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Paid parking - UNIPARK and ParkTown. Read instructions

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (Bičiulių g.36)
Bičiulių g. 36, Vilnius
Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (Šeimyniškių g. 19C)
Šeimyniškių g. 19C, Vilnius
Hila
V. Grybo g. 32A, Vilnius, Lithuania
7:00 - 20:00
MRT examinations performed until 21.00
8:00 - 15:00
MRI examination schedule - 7.00-19.00
9:00 - 15:00
Only MRI examinations!
The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free parking to the right of the building. Drive up to the barrier, wait for the guard to lift it, and enter the site.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Family Medicine
Estų g. 1, Vilnius
8.00–20.00 val.
The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free car parking is available in the shopping center's lot.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Family Medicine
Laisvės pr. 10A, Vilnius, Lithunia (B building)
8.00 - 20.00

The laboratory closes 30 minutes earlier than indicated.
Free parking - in reserved places in front of the entrance to the center.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Šeimos medicinos centras (Bičiulių g.36)
Bičiulių g. 36, Vilniaus r. sav.
07.00 – 20.00 val.
nedirbame
Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (V. Grybo g. 32A)
V. Grybo g. 32A, Vilnius
7.00–20.00 val.
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Free car parking is available on the right side of the building.
Drive up to the barrier, wait for security to lift it, and enter the parking lot.

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine
Lvivo g. 101, Vilnius, Lithuania
8.00 - 20.00
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Paid parking - UNIPARK and ParkTown. Read instructions

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine
Estų g. 1, Vilnius
7.00-20.00 val.
9.00-15.00 val.
Please arrive in sportswear for the physiotherapy session and certain tests.
Paid parking - UNIPARK and ParkTown. Read instructions

All of the center's medical service facilities are accessible for people with disabilities.
Hila | Reabilitacijos ir sporto medicinos centras (Bičiulių g.36)
Bičiulių g. 36, Vilnius
- Doctors
-
Services and prices
Examinations Ophthalmology (eye care) Orthopaedics and traumatology Obstetrics and Gynaecology Rehabilitation and sports medicine Treatment of ear, nose, throat (ENT) disease
-
For patients
How to make an appointmentYou can make an appointment at our Centre by all common methods.What to take care about before arrivingOur personnel will inform you what documents you should have at arrival.What to do at arrival to the CentreAt arrival to the centre please print a ticket at the ticket terminal.Payment and servicesPossible payment by leasing, according to the contract, compensation.Accommodation and mealsOur clinic is located about 3 km from the Vilnius city centre.International patientsThis information is for international patients.Confidentiality assuranceWe understand how are important your personal data.How to arrive to the CentreYou can reach our Center by transport.
- Testimonials
- Articles
- Gift vouchers
Knee cartilage repair surgery
An effective and reliable treatment




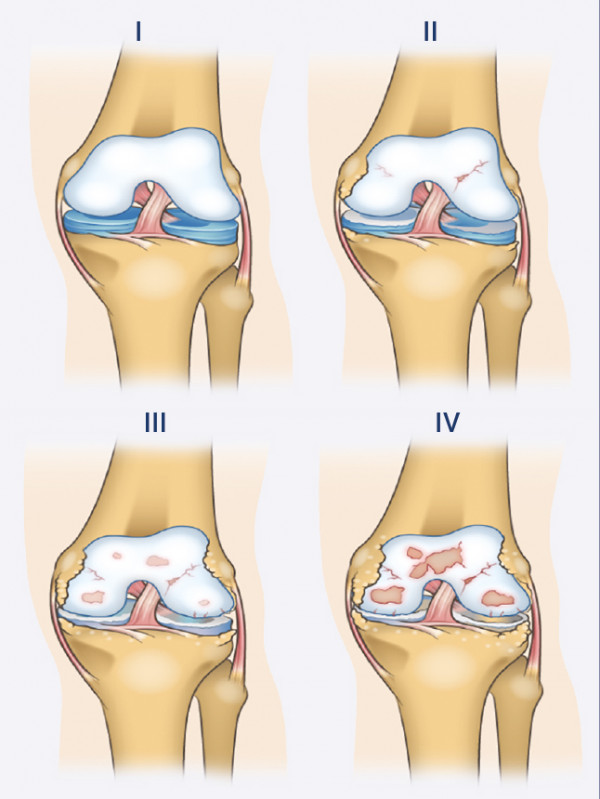
Knee articulate cartilage repair is a reliable solution for patients who want relief from the discomfort caused by the following symptoms: gnawing ache or pain in the knee joint, “crunching” sound, “locked” sensation and swelling. The surgery is also recommended for osteoarthrosis sufferers (also called arthrosis, osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease), which manifests itself in damage to the articulate cartilage, the surrounding soft tissue and the bones.
We offer the following treatment options for conditions involving damaged cartilage: medicines, kinesiotherapy, physiotherapy, injections (corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid, PRGF, nStride, stem cell therapy). When none of the above work, or when the damage to the cartilage is extensive, surgical treatment is recommended.
The knee cartilage repair surgery performed at our Centre uses the most advanced techniques: spongialization + covering with coagulated plasma (we are the only centre in Lithuania performing this unique cartilage restoration surgery!), scaffold, membrane assisted surgery, which we perform most frequently, arthroscopic surgery, arthroscopic microfracture surgery, natural cartilage repair – Matrix-Induced Chondrocyte Implantation (MACI), autologous osteochondral transplantation/mosaicplasty, mesenchymal stem cell treatment.
A number of factors determine which cartilage repair method is the most suitable for each individual case. If the pain has been bothering you for several weeks or more, make sure you get an appointment to see your doctor. Any delay may limit the choice of the possible treatment options.
Knee cartilage repair surgery price
| Service | |
|---|---|
|
Arthroscopic Surgery of the joint
|
|
|
Arthroscopic Surgery of the joint
|
|
|
Arthroscopic Surgery of the joint
|
| Service | |
|---|---|
|
Membrana (2x2)
|
|
|
Platelet-rich plasma (PRGF) preparation and injection
|
|
|
The tube for platelet-rich plasma preparation (PRGF)
|
What factors affect the price?
The prices indicated below apply to citizens of the Republic of Lithuania and the European Union.
If you are coming from another country please check the price by telephoning or sending an email.
What you need to know about surgery?
Spongialization technique for knee cartilage repair (covering with coagulated plasma) is the standard arthroscopic surgery. The optical devices are inserted through small incisions, the joints are examined from the inside and the damage to the cartilage, including the size of the affected area, are assessed.
The patient’s own blood is prepared and processed, it is separated out to create platelet and growth factor rich plasma which is then combined with the healthy cartilage fragments and coagulated using a special method. A solid plasma and cartilage mixture transplant is then attached to the defected area of the cartilage.
If the area of the damage is not extensive, i.e. only a few cm2, the surgery is minimally invasive and is performed through small incisions. If the damage to the cartilage is extensive, a 5-7 cm incision is made to allow for the defected area to be properly covered. No additional membranes or synthetic gels are used for this purpose.
The surgery takes about one hour and we are the only centre in Lithuania that performs it!
Scaffold, membrane assisted surgery is the most common surgery. Scaffolds and membranes are natural polymers, collagen, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin-6-sulfate, silk fibroin. These are biologically active substances, that encourage cell adhesion and growth. During the surgery, one of these membranes is transferred to the joint and attached to the healthy cartilage. New healthy cartilage cells start being produced and the damaged cartilage tissue is restored.
Arthroscopic surgery is suitable for patients who have been diagnosed with grade 1-2 chondromalacia with small cartilage defects, and grade 3-4 osteoarthrosis. The damaged cartilage, loose bodies etc. are removed during the operation.
Arthroscopic microfracture surgery can be performed on small – 1-2 cm2 cartilage defects.
During the surgery, multiple holes, or microfractures are made, the bone marrow cells and blood from the holes combine to form a clot, which is rich in protein and specific cells that are able to regenerate. It is used to cover the defective area. A healthy hyaline cartilage forms in approximately 4 months.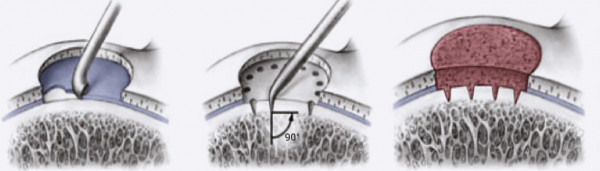
Matrix-Induced Chondrocyte Implantation (MACI) is a natural method that can regrow the cartilage. During the surgery a small sample is taken from the patient’s healthy cartilage, which is then transported to laboratories in Germany. The cultivated cartilage is implanted in the defective area. It is a two-step procedure which is not performed very frequently as we prefer not to perform more interventions than necessary.
Autologous osteochondral transplantation/mosaicplasty is performed when osteochondral damage is <4 cm2. It is suitable for young and active patients.
During the surgery, the damaged cartilage is replaced with osteochondral allograft or autologous transplant. 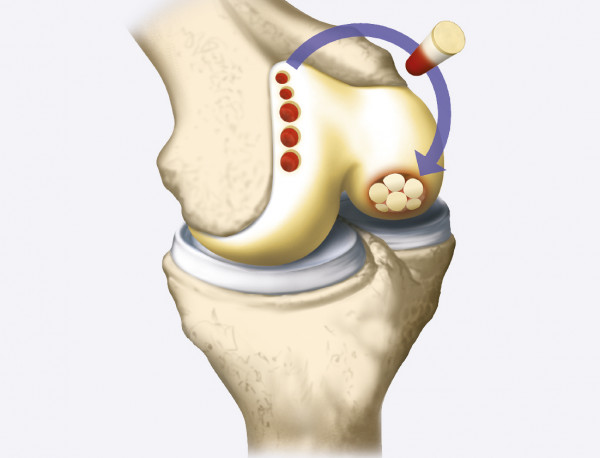
Mesenchymal stem cell treatment
The Lipogems technology is used to obtain stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow or fat tissue, and these are then injected into the damaged area of the articular cartilage. This aids the regeneration of the cartilage.
Following the surgery you will stay in hospital for 24 hours under the observation of our medical staff. You will leave the hospital on crutches and will continue using them for up to 6 weeks.
During the recovery period it is essential to protect the newly formed cartilage from any trauma, therefore you will have to use crutches for up to 6 weeks, gradually increasing the load on the operated limb. Patients are referred for rehabilitation treatment (exercises at home and/or in the gym and/or in the pool; massages, bicycle, treadmill). Following the surgery, the patients have to work on increasing their muscle strength, and aid the regeneration and formation of the cartilage. Patients can return to their full sports routine 13 weeks after surgery.
With a gradual and correct increase of physical load, the patient can again get involved in their favourite physical activities 7-12 months following the surgery.
Tests required before the surgery:
-
Complete blood count;
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT);
-
Blood glucose test;
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG) including interpretation.
Patients can bring their test records from other healthcare institutions, or they may have them done at the Medical Diagnostic and Treatment Centre. The tests take 2 hrs. Prices of the tests performed at the Centre. The tests must be performed no earlier than 14 days before the surgery.

4 reasons
for choosing us
-
We can perform the required tests and confirm the diagnosis in 1 day.
-
Surgery can be performed within 2-3 weeks after the consultation. You can travel by plane the day after the surgery.
-
Surgeries are performed by one of the most experienced surgeons in Lithuania.
-
Hospital acquired infection rate – 0 in 5 years.
Doctors
Rimas Darijus
Orthopaedic traumatologist
-
LT, EN
-
Working hours
Frequently asked questions
The knee cartilage can become damaged for a number of reasons, but in most cases it is caused by trauma. It can be any type of trauma, such as acute momentous trauma, sports trauma, falling over, twisting the joint in an awkward way, a car accident or another high impact trauma. The damage can be also caused by long-term impact, e.g. prolonged walking or running. If you have not been physically trained to deal with such a load, and your knee has not been subjected to it before, the cartilage may be too weak to endure it and can become damaged.
Cartilage damage is also associated with obesity, when the joints have to carry too much weight, hormonal imbalance and autoimmune diseases.
Injured muscles and tendons, as well as fractured bones have the ability to heal and grow back together. However, because cartilage tissue does not contain blood vessels or nerves, its chances to regenerate or heal are very limited.
MRT (magnetic resonance tomography) is the main test, as it presents images of soft tissue and cartilage. It is used to assess the condition of tendons and menisci, the location of the cartilage damage, the size and depth of the affected area, and the condition of the surrounding bone. This helps in the selection of the treatment options and surgery method.
The surgery technique and method depend on the extent, place, depth of the damaged area, its origin, as well as the age and profession of the patient (normally patients have to be under 50). Spongialization, which is a method of articulate joint restoration, when a coagulated plasma transplant is formed using the patient’s own blood, is more suitable for recent injuries and when there is substantial healthy cartilage that can be used for surgery. All the above factors play an important role when it comes to good surgery results.
The conservative treatment methods: physiotherapy, kinesiotherapy, anti-inflammatory and pain reducing treatments, hyaluronic acid, plasma, steroid injections are used when the cartilage defects aren’t deep, or are superficial. Certain life-style changes can also be recommended, such as weight monitoring, changing of sports or work activities.
Other cartilage regeneration methods are recommended for older patients. When the cartilage damage is extensive and the osteoarthrosis is in the advanced stages, we recommend joint replacement or endoprosthetic surgery.
If the damage consists of a full-depth cartilage defect, surgery to restore the damaged cartilage is performed. Different surgery techniques may be used: marrow stimulating techniques, microfracture surgery, osteochondral transplantation, mosaicplasty, use of cartilage bone transplant, autologous chondrocyte implantation, use of collagen membranes, and autologous cartilage tissue implants. Only an experienced doctor can determine which method is best for each individual.
As with any other disease, we risk causing even more damage to ourselves if we fail to seek help in good time when confronted with cartilage, tendon and menisci injuries. The untreated problem leads to osteoarthritis – a degenerative disease of the joint, which may end up in disability.
Statistics show that 5-10% of people over 40 have a deep cartilage defect. That means that the condition affects every 5th to 10th person. In older age, with the progression of the disease, approximately 80% of patients over 75 suffer from the degenerative joint disease – osteoarthritis.
The situation is even worse in the world of professional sports: in up to 38% of contact sports, such as basketball, football and rugby, players are diagnosed with cartilage defects. Following the surgery, only 45-78% of athletes return to their previous physical form.
The price depends on:
- scientific degree of the preferred physician,
- preferred substances and their amounts required for a specific service,
- applied anaesthesia,
- nursing type and number of in-hospital days.
- preferred type of catering,
- availability of referral letter.
The Centre standard price is applied if you have a properly issued referral letter.
The regular price is applied if you do not have a referral letter.
You do not need a referral letter for laboratory tests, the Regular Price is applied.
How soon are the results of laboratory tests available?
2 hours for the most common (routine) blood tests and urinalysis.
3 hours for tests ordered before 9.00 a. m.
If rare tests are ordered for a single sample that require stopping the analyser to change test reagents, the time to have the test done may be prolonged by several additional hours. 10 to 20 working days, if samples are to be sent to Germany, the time required for the test to be done depends on the complexity of the test.
The reports of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) imaging and other
instrumental examinations are usually ready immediately, i.e within 2-3 hours after the examination.
The report of a test which is carried out on Saturday is available from the healthcare professional carrying
out the test (usually the report is ready within 3 working days).
The reports of echoscopic and other examinations that are carried out in the physicians office are issued
immediately after the examination.
Regular price
This price applies to patients not covered by compulsory health insurance, who do not have a referral letter from their doctor (except radiological examinations, for which a referral letter is mandatory); when the referral letter does not meet the requirements defined by the legal acts; when the disease is not included in the list of reimbursable diseases; when the referral letter has expired (30 days), and in other cases indicated in the Rules for the Provision and Payment of Commercial Personal Healthcare Services approved by Order No. 357 of the Minister of Health dated 30 July 1999 (with subsequent amendments), the patients should pay for such services themselves.
Should the patient chose particular implants or substances or order individual menus, these will incur additional costs.
What does the service price comprise of?
The price of an instrumental examination consists of the price of the examination and the required materials (contrast medium, injections of the contrast medium, anaesthesiological care, imaging, etc.). The prices of the specific service are available at Reception.
The price of blood laboratory tests is comprised of the test price (indicated in the pricelist) and the price for collecting the blood sample. If a swab is required to carry out a test, this may sometimes incur additional costs. The prices of the specific services are available at Reception.
In the case of surgical treatment additional costs for anaesthesia, implants and substances preferred by the patient as well as individually chosen menus are applied.
In the case of dermatology services only the price for the physician's service is indicated. The total price of a dermatology service includes the price of the procedure and all materials required for the procedure. The prices of the specific services are available at Reception and/or during the consultation with the physician.
The price of a basic procedure is the lowest procedure price. The actual price is discussed during the consultation before the procedure considering the extent and complexity of the procedure.
Notes
For the price of services provided at the Centre outside working hours, ugently, at night, while on holidays or without a referral letter, or that require the presence of physicians not continuously employed by the Centre, please enquire in advance.
The Centre may change the price of services without warning, as well as offer new services, change the content of existing services or refuse to provide certain services.
What factors affect the price?
Centre standard price
For consultations and examinations with a referral letter
According to the Law on Healthcare System of the Republic of Lithuania (part 5 of article 49), if patients prefer to receive more expensive services, materials and procedures, they must pay the difference between the factual price of these services, materials and procedures and the price of the services, materials and procedures that are provided free of charge following the rules defined by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Lithuania. If patients who are entitled to receive personal healthcare services free of charge prefer to receive additional services or procedures, they must pay for these services or procedures themselves.
The prices presented here are developed according to the Centre Standard which is used while providing high quality integrated and coordinated healthcare services, ensuring patient safety and expedition, integrity of service provision, and effective examination using equipment from reliable manufacturers, newest generation products associated with minimal side effects, and providing the best nursing care.
For example, the colonoscopy procedure is carried out with minimal discomfort to the patient as they are “asleep” during the procedure, i.e. anaesthesia is used during the procedure, and the procedure is continuously monitored by a physician endoscopist and physician anaesthesiologist-reanimatologist.
The price for computed and magnetic resonance tomography scans following the rules established by the Ministry of Health are different in all 5 Territorial Departments of the Health Insurance Fund (HIF). The specific prices are available at Reception.
The price for a consultation with a physician depends on the scientific degree of the selected physician.
This price does not apply to Laboratory tests. The same price is applicable for all patients, irrespective of whether they are covered by public health insurance or have a referral letter from their physician. The price of blood laboratory tests is comprised of the test price (indicated in the pricelist) and the price for collecting the blood sample.
Centre standard price
For surgeries and surgical procedures with a referral letter
For patients who are covered by compulsory health insurance, and have a referral letter from their doctor for the procedure or surgery; any services that are reimbursed from the budget of the compulsory health insurance fund are provided free of charge, except for cases indicated in the Rules for the Provision and Payment of Commercial Personal Healthcare Services approved by Order No. 357 of the Minister of Health dated 30 July 1999 (with subsequent amendments), when patients themselves should pay for such services.
This price applies to patients covered by compulsory health insurance, who have a referral letter from their doctor for the procedure or surgery; the price covers the costs of closely related services necessary for therapeutic purposes that are specified in certain specific cases while providing healthcare services.
Should the patient chose particular implants or substances that are not reimbursed by the compulsory health insurance fund, or they want to have more expensive services or substances for which only the basic price is reimbursed, these as well as any price difference or individual catering menus will incur additional costs.
What does the service price comprise of?
The price of the consultation with a physician comprises of:
- Discussion with the patient – listening to the complaints and taking the patient’s’ medical history (patient provides information to the physician about their health).
- Examination and condition assessment.
- Preliminary diagnosis.
- If indicated, development of an examination and consultation plan (necessary examinations are prescribed and the patient is referred for consultations with other specialists).
- Interpretation and assessment of test results.
- Making and confirmation of the diagnosis.
- Development and implementation of the treatment plan, appointment and discussion about the surgery.
- Recommendations for treatment, nursing, work and care in an out-patient setting.
The final price of the surgery is established by summing up the prices of surgery, anaesthesia, implants, care in the ward (from Day 2), catering price according to the menu preferred by the patient and the price of certain substances. The specific extent of the surgery and its price is discussed before the surgery during the consultation with the surgeon, considering the complexity of the surgery, its duration and the patient's health status.
The price of an instrumental examination consists of the price of the examination and the required materials (contrast medium, injections of the contrast medium, anaesthesiological care, imaging, etc.). The prices of the specific services are available at Reception.
The total price of vaccination services consists of the price of the consultation with a physician and the price of the vaccine. The prices of the specific service are available at Reception.
Example: If you come for a Vaxigrip vaccination, the service price will be calculated as follows:
Vaccination (not including vaccine price) – 6.22 (for those covered by insurance) – 8 Eur (for those NOT covered by insurance)
Influenza vaccine – 12.68 Eur.
In total: 6.22+12.68 = 18.90 Eur or 8+12.68 = 20.68 Eur.
There is no need for a consultation with a physician for influenza and tick born encephalitis vaccinations.
In all other cases a consultation with a physician is mandatory and involves additional costs.
However, if you are referred for a vaccination by another physician and have a referral letter, you do not need to have a consultation with one of our physicians. Please note however that the referral letter for vaccination is only valid for 24 hours from the time it is issued. The vaccine required should be indicated in the referral letter.
The above calculation is presented using conditional numbers.
Notes
For the price of services provided at the Centre outside working hours, urgently, at night, while on holidays or without a referral letter, or that require the presence of physicians not continuously employed by the Centre, please enquire in advance.
The Centre may change the price of services without warning, as well as offer new services, change the content of existing services or refuse to provide certain services.
Teminiai naujienlaiškiai
-Gydytojų patarimai;
-Specialios akcijos tik prenumeratoriams.


